Climate Pollution in Baton Rouge
How is climate pollution affecting Baton Rouge?
The Capital Region has been severely impacted by extreme weather related to climate pollution—from the catastrophic floods of 2016 that damaged over 60,000 homes and killed 13 people to the record-breaking hot weather in July and August 2023 that killed 69 Louisianans and caused many more health-related illnesses.
We will continue to see high levels of rainfall, searing weather, and more intense and unpredictable hurricanes, with consequences for our safety and wellbeing. The sea level is also rising, raising the high-tide and eroding coastal areas across Louisiana.
What kind of climate pollution is emitted in Baton Rouge?
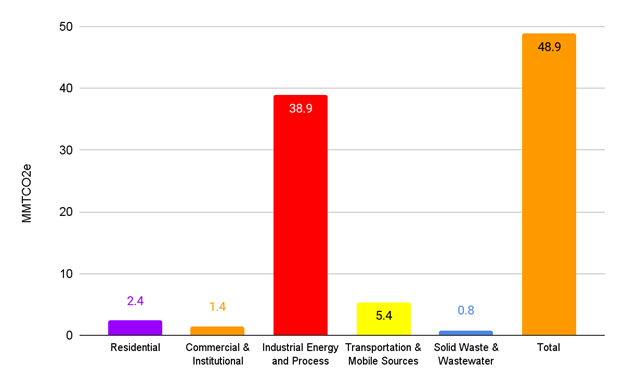
The Baton Rouge MSA emits 49 million metric tonnes of greenhouse gasses—measured in terms of carbon dioxide equivalence (MMtCO2e)—annually. The majority of these emissions (80%) are from industry, including fossil fuels for industrial processes and emissions from agriculture. The remainder are generated by cars and other gas vehicles (11%) powering buildings with coal and natural gas (3%), and solid waste (1%).
Source: SSG analysis